Environment by Branch in Harness Database DevOps
Harness Database DevOps supports managing database changes using environment-specific branches. This approach allows you to maintain different configurations for development, staging, and production environments directly in your Git repository.
Why Use Environment Branches in Harness Database DevOps?
Here are several reasons why teams opt for a branch-per-environment strategy:
- Consistency with Application Deployment: If you're already managing app deployments using environment-specific branches, aligning your DB changes keeps both layers synchronized.
- Environment-Specific Configurations: Maintain isolated configurations or schema changes for dev, staging, and production environments.
- Controlled Progression: Promote and test changes in lower environments before merging them into production.
- Audit Trail: Each branch maintains a commit history that improves traceability and accountability for schema changes.
What Are the Tradeoffs of Branch Per Environment?
While beneficial, this approach introduces some complexity:
- Increased Complexity: Managing multiple branches requires rigorous Git hygiene.
- Potential for Drift: Without strict coordination, environments can diverge.
- Merge Conflicts: More branches = more chances for conflict.
- Overhead: Requires additional team effort to maintain branches and reviews.
- Unintentional Promotion of Dev-Only Changes: If you're managing dev/staging-only changes (like test tables or mock data), they may unintentionally get merged into higher environments.
::: note
Recommendation: Use the context field on the database instance to restrict execution, even when the change exists in the branch. You can adopt this model if your application deployment already follows a branch-per-environment structure—ensuring consistency across the stack.
:::
How to Configure
Follow these steps to configure environment-based deployments in Harness Database DevOps:
1. Set Up Your Git Branches
Create separate branches in your Git repo for each environment: development, staging, production, etc.
2. Define Schema Configuration per Branch
- Go to Database DevOps and Click on Add DB Schema.
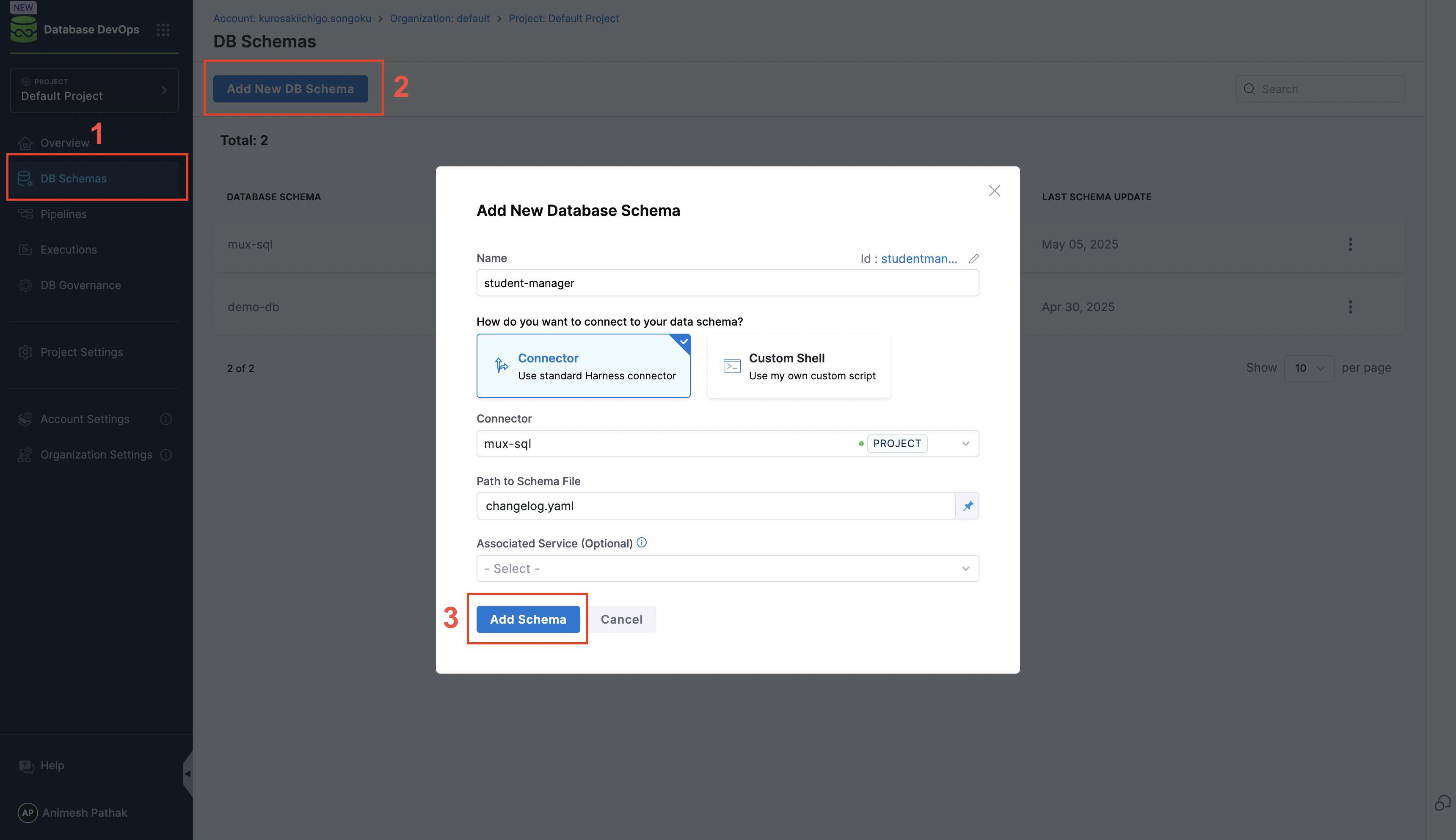
3. Create a Database Instance
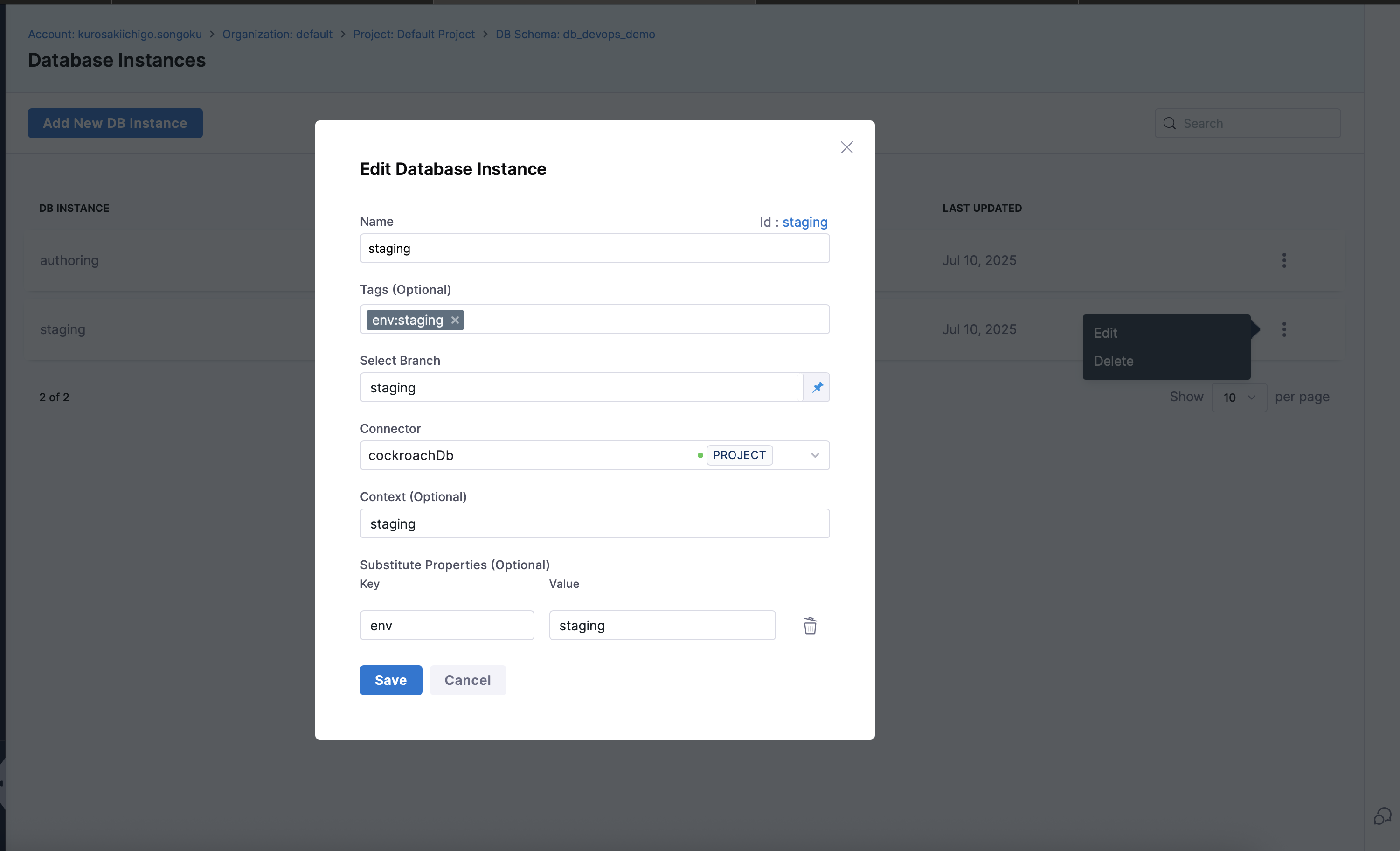
- Select the Database Schema and click on Add DB Instances in Harness.
- Create a new instance for each environment.
- Attach the appropriate JDBC connector and context labels.
4. Configure a Git Trigger
- Navigate to Pipeline Studio > Triggers.
- Add a new Git trigger that listens for changes on each environment branch.
- For example,
devtrigger watchesdevbranch merges.
-
Select the Git repository and specify the Event type (e.g.,
Push).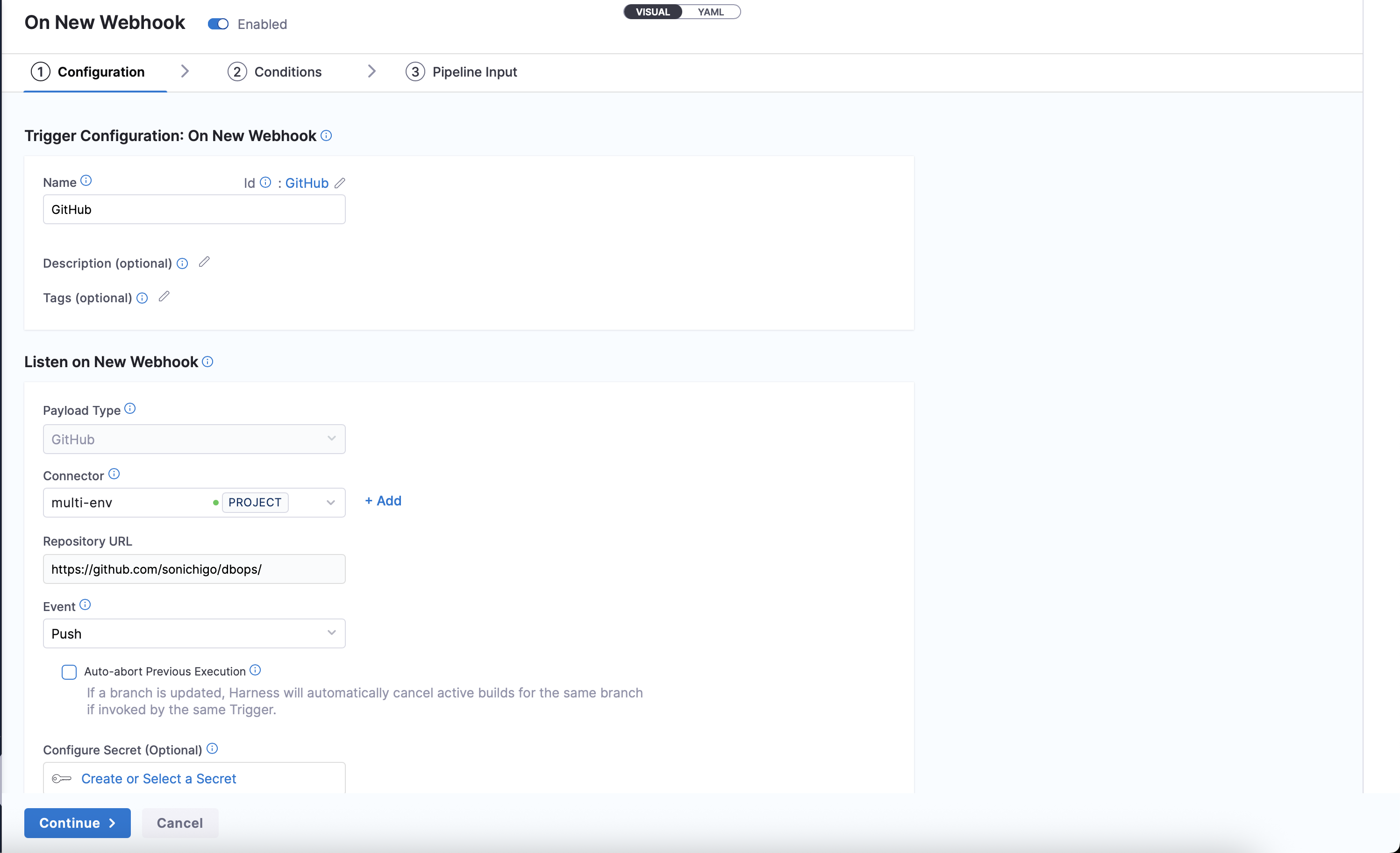
-
Click on Continue and Configure the conditions for the trigger:
- Branch Name: Specify the branch to watch (e.g.,
dev,staging,prod). - Changed Files: Optionally, specify file patterns to filter changes (e.g.,
schemas/*.sql).
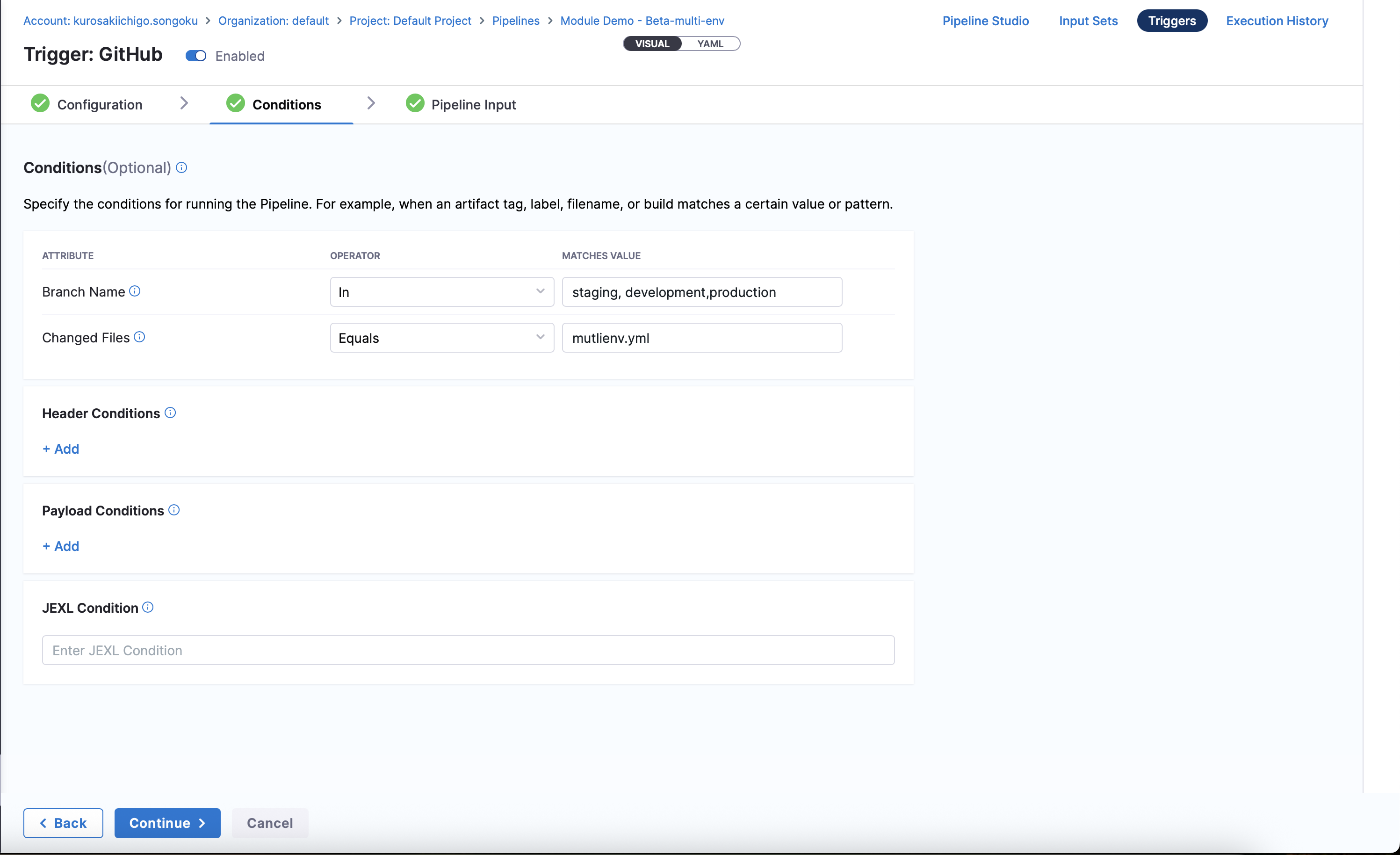
- Branch Name: Specify the branch to watch (e.g.,
-
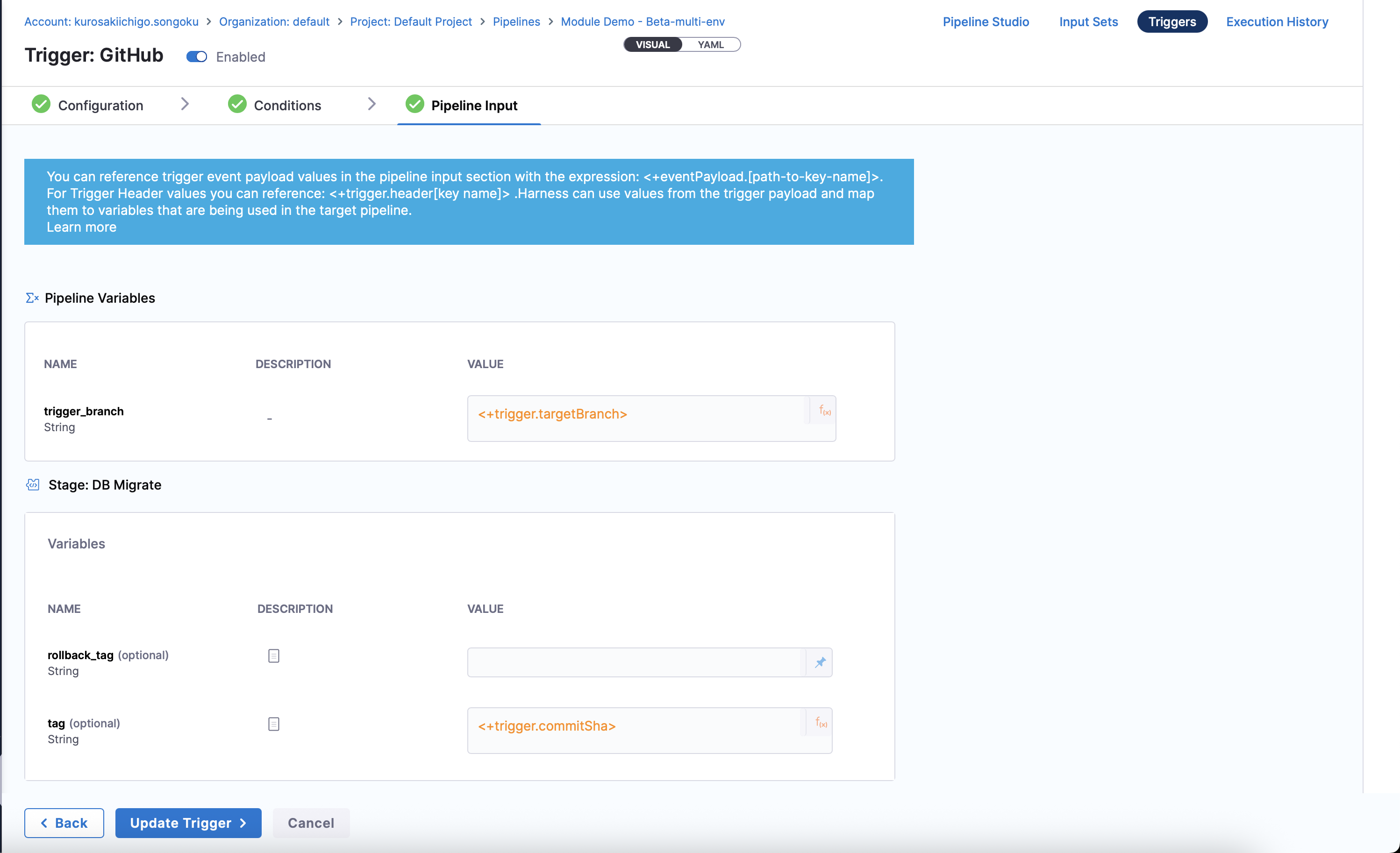
Enter the Pipeline Inputs that the trigger will use:
- Trigger Branch: This is the branch that the trigger will monitor.
- Rollback Tag (Optional): Optionally, specify a tag to use for rollbacks.
- Tag (Optional): Optionally, specify a tag to apply to the deployment.
::: note You can learn more about triggers in Harness Database DevOps Learn how to configure Git triggers → :::
5. Design Your Pipeline
- In Pipelines, create a pipeline that includes a
DBSchemaApplystep. - Set up the pipeline to:
- Deploy using the associated schema and DB instance.
- Apply only the changes in that branch.
- Optionally include approvals, rollback, and verification steps.
- Visual Overview
- YAML Overview
pipeline:
identifier: Module_Demo_Betamultienv
projectIdentifier: default_project
orgIdentifier: default
stages:
- stage:
identifier: DB_Migrate
type: Custom
name: DB Migrate
description: "Deploy DB Schema to multiple environments"
spec:
execution:
steps:
- parallel:
- stepGroup:
identifier: Liquibase_Update_staging
name: Update Staging
steps:
- parallel:
- step:
identifier: Apply_To_Staging
type: DBSchemaApply
name: Apply To Staging
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
resources:
limits:
memory: 500Mi
cpu: 400m
dbSchema: db_devops_demo
dbInstance: staging
tag: <+stage.variables.tag>
timeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Success
condition: <+pipeline.variables.trigger_branch>
== "staging"
stepGroupInfra:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: db
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
initTimeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Success
condition: <+stage.variables.rollback_tag> == "" || <+stage.variables.rollback_tag>
==null
- stepGroup:
identifier: Liquibase_Update_prod_us
name: Update Production-us
steps:
- step:
identifier: Apply_to_Production_us
type: DBSchemaApply
name: Apply to Production-us
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
resources:
limits:
memory: 500Mi
cpu: 400m
dbSchema: db_devops_demo
dbInstance: authoring
tag: <+stage.variables.tag>
timeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Success
condition: <+pipeline.variables.trigger_branch> == "staging"
stepGroupInfra:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: db
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
initTimeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Success
condition: <+stage.variables.rollback_tag> == "" || <+stage.variables.rollback_tag>
==null
delegateSelectors:
- cockroachdb-delegate
rollbackSteps: []
serviceDependencies: []
tags: {}
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors: []
action:
type: Abort
variables:
- name: rollback_tag
type: String
description: Specify this if you wish to rollback to the particular tag
required: false
value: <+input>
- name: branch
type: String
description: ""
required: true
value: main
- name: changelogfile
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: example-changelog.yaml
- name: tag
type: String
description: Argument to Liquibase Tag Command
required: false
value: <+trigger.commitSha>
- name: server_jdbc_url
type: String
description: JDBC URL of the target server
required: false
value: <+pipeline.variables.server_jdbc_url>
- name: arch
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: latest
delegateSelectors:
- cockroachdb-delegate
when:
pipelineStatus: Success
tags:
demo: ""
variables:
- name: server_jdbc_url
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: jdbc:sqlserver://<+variable.sql_server_ip_address>;database=MyTestDataBase;trustServerCertificate=true
- name: user
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: <+secrets.getValue("mysql_sa_user")>
- name: trigger_branch
type: String
description: ""
required: true
value: <+trigger.targetBranch>
name: Module Demo - Beta-multi-env
6. Manage Promotion Between Environments
- Use Git pull requests to promote changes between branches. e.g.,
dev→stagingorstaging→prod - Harness will auto-detect the merged changes via the trigger and deploy accordingly.
Conclusion
Deploying by environment branches in Harness Database DevOps provides alignment with traditional application deployment strategies and gives teams clear separation of concerns. While it introduces more Git management overhead, it enables safer promotion paths and more isolated testing.
Just ensure to manage drift carefully, use contexts to limit dev-only changes, and maintain strong PR discipline when promoting between branches.